I have developed “Chatur Framework”, an easy 5 step process to make a good stock investment. Chatur is a Bengali word that translates to clever. Our investment framework will guide you to find great businesses and invest in their stocks.
Every investment you make must fulfill a goal. If you are looking for the hottest stocks that will make you very rich in a quick time then you should not use our framework. Our investment process helps you to find individual stocks that have a relatively lower risk of permanently losing your capital than many stocks in the broader index.
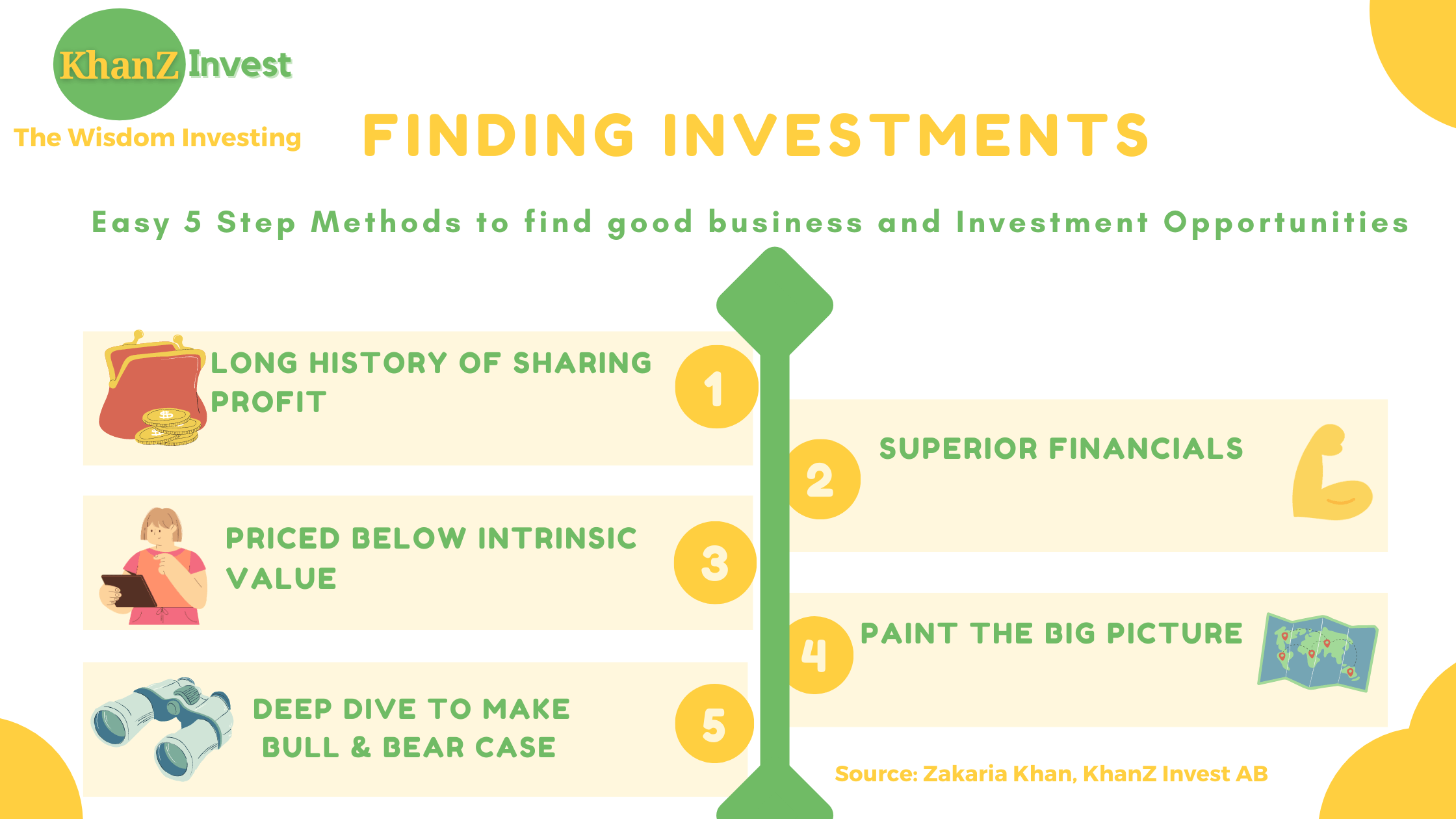
What are the 5 steps investing process of Chatur Framework?
I developed a process to invest in good quality businesses that have superior financials, a strong business presence, and long-term future prospects. The aim is to help you better control your investment risks and at the same time generate good long-term returns.
- 1: Filter out Superior financials, must have strong cashflow and good profitability
- 2: Check for Long term compounder, must have a history sharing profits with it’s shareholders
- 3: Calculate Margin of Safety, Business Intrinsic Value should be lower than the stock price
- 4: Paint the big picture, must have a strong market presence and future prospects
- 5: Make a bull & bear case, market downturn mitigation process
I gave a detailed explanation of each step with examples
What are the principles of Chatur Investing Framework?
Chatur Framework is based on value investing principles. In a nutshell, value investing means we strictly evaluate the quantitative matrixes of the business calculate the intrinsic value of a business, and buy its stocks at a cheaper price. Buying stocks cheaper than their intrinsic value is known as the margin of safety.
Our investing framework is not limited to quantitative matrixes, we equally value qualitative measures of a business. Step 4 & Step 5 of the Chatur Investing Framework looks into the qualitative measures of the business.
What are the charectaristics of a good busniess?
Each investment opportunity is unique and we evaluate case by case. There is no fixed formula but often good businesses share some common characteristics. I listed some traits we look for in a business when evaluating it for a potential investment.
- Good Profitability
- Strong Financial Health
- Long term Growth
- Paying Dividend
- Buy Back Shares
- Reinvest to increase the share price
- A strong barrier to entry
- Power to Increase product price
- Long term demand and growth
- Transparent and capable Management
Step 1: Superior Financials
The stock you are investing in must have a financially sound underlying business. A business might have a very good long-term future and can be selling for cheap but if it does not have sound financials today then it can go bankrupt and you may lose all your capital.
Businesses that generate strong cash flow often also have good financials. To generate cash flow, the business must be good profitability and sales. In our 5 steps process, we look for that first.
We consider Profitability, Liquidity, Solvency, and Growth to be the four cornerstones of a good healthy business. When a business shows good positive numbers in all four cornerstones, we identify that the business has Superior Financials. I only want to invest in businesses with superior financials.
To evaluate the financial health of a business we look into some important ratios. Below I am listing those.
- Ratios to check the profitability of a business
- Return on Equity (RoE)
- Return on Assets (RoA)
- Net Profit Margin
- Return on Capital Invested (RoIC)
- Earning Yield
- Ratios to check the liquidity of a business
- Quick Ratio
- Current Ratio
- Cash Ratio
- Rotios to check the solvancy of a businessInterest Coverage
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt to Asset Ratio
- Long Term Debt to Total Asset Ratio
- Growth parameters of a business, calculate 3-5 years CAGR
- Revenue
- EBITDA
- Earning Per Share (EPS)
- Free Cash Flow (FCF)
- Cashflow from Operation (CFO)
- Free Cash Flow to Firm (FCFF)
- Free Cash Flow to Equity FCFE
“Losing Capital is the Achilles heel for Compounding. Protect your Capital by reducing Bankruptcy Risk”
Zakaria Khan
Superior Financial data check with AT&T example?
Personally, I use 5 years of data and even more parameters. Below, I am giving you an example of how I compare ratios using AT&T’s last 5 years’ financial data.
Profitability ratios of AT&T
| Years | Earnings Yield | ROA | ROE | ROIC | Net Margin |
| 2020 | -2.5% | -1.2% | -3% | -1.08% | -3.13% |
| 2019 | 4.83% | 2.52% | 6.88% | 4.10% | 7.67% |
| 2018 | 10% | 3.64% | 9.99% | 5.39% | 11.34% |
| 2017 | 12.21% | 6.63% | 20.74% | 9.74% | 18.34% |
| 2016 | 4.92% | 3.21% | 10.46% | 5.38% | 7.92 |
| 5 Y Average | 5.88% | 3% | 9.01% | 4.71% | 8.43% |
| 5 Y Median | 4.92% | 3.21% | 9.99% | 5.38% | 7.92% |
Growth ratios of AT&T
| Year | Revenue | EBITDA | EBIT | CFO | EPS | FCFF | FCFE | FCF |
| 2020 | 171,760 | 34,921 | 6,405 | 43,130 | -0.75 | 38,058 | 40,146 | 27,455 |
| 2019 | 181,193 | 56,172 | 27,955 | 48,668 | 1.89 | 35,862 | 15,705 | 29,033 |
| 2018 | 170,756 | 54,526 | 6,096 | 43,602 | 2.85 | 28,734 | 34,480 | 22,351 |
| 2017 | 160,783 | 45,336 | 19,970 | 39,151 | 4.77 | 30,022 | 58,434 | 17,601 |
| 2016 | 163,783 | 46,801 | 24,347 | 39,344 | 2.10 | 20,240 | 14,298 | 16,936 |
| 5 Y Average | 169,608 | 47,551 | 20,955 | 42,779 | 2.17 | 30,583 | 32,613 | 22,675 |
| CAGR till 5Y Avg. | 0.7% | 0.32% | -2.96% | 1.69% | 0.68% | 8.61% | 17.93% | 6.01% |
Liquidity Ratios of AT&T
| Year | Current Ratio | Quick Ratio | Cash Ratio |
| 2020 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.15 |
| 2019 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.18 |
| 2018 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.08 |
| 2017 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.62 |
| 2016 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.11 |
| 5 Y Average | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.23 |
| 5 Y Median | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.15 |
Solvency ratios of AT&T
| Year | Debt/Asset | Debt/Equity | LT Debt/Total Asset | Interest Coverage |
| 2020 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.29 | 0.81 |
| 2019 | 030 | 0.81 | 0.27 | 3.32 |
| 2018 | 0.33 | 0.91 | 0.31 | 3.28 |
| 2017 | 0.37 | 1.16 | 0.28 | 3.17 |
| 2016 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 4.96 |
| 5 Y Average | 0.33 | 0.97 | 0.29 | 3.11 |
| 5 Y Median | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.28 | 3.28 |
Unless a business has a long history of sharing its profit with shareholders, I generally would not invest in them. 3 Key reasons why a business may not share profits are as follows
- Business is Non-Profitable or unable to create necessary values
- Business is declining.
- Management incentives are consuming profits
High growth companies often promise to be very profitable in the future. You should pay a premium price for the growth aspect of the business but wait until they become profitable and prove their business model. Not all future promises are fulfilled and I don’t have a crystal ball that can predict the future.
“Not all ugly ducklings turn into Swans. Avoid ugly ducklings, buy Swans directly“
Zakaria Khan
Let’s say the business you have invested in is the most profitable and innovative in the world. If they don’t share profits with you then as an investor there is no reason for you to invest your money in that business.
A sign of a good business is that it is a long-term compounder. This means, the business has been generating shareholder values and distributing that profit for a long time. Profits generated from a business are the right of its shareholders/owner.
Businesses can return their profits to its shareholder in 3 different ways:
Distribute cash dividend
The company can distribute a certain percentage of its annual net profit as cash to its shareholder.
If a business makes a net profit of 100 and gives 50 back to its shareholders then the payout ratio is 50%. A reasonable/low payout ratio tells us that this dividend is safe. If next year the company makes 75 profit then it can still pay 50. The rest of the money can be used for future growth
The share buyback is another way a business return value to the shareholder. What that means is that company is buying back its own shares and then destroying those shares. This way our ownership in the company increases without spending any more money.
For example, let’s say a company has 100 shares outstanding. You bought 1 share, so your current ownership in the company is 1%. Now, let us assume that the company bought back 50 shares in the next 5 years. Now, after 5 years they have only 50 shares outstanding and you still own your 1 share. This means, now you own 2% of the company.
Additionally, since the share count of this company is now half, they will have to pay dividends only for the remaining 50 shares. So, the business can retain more income which will improve their financials.
Further, they can increase the cash dividend payout amount on the remaining 50 shares. Buyback is also a more tax-effective way for businesses to return a profit to the shareholders.
Retain earnings for rapid growth
Sometimes, we can see that a business retains all of its profit. They don’t give it back to the existing shareholders. The only justification for this behavior is that the business is using the profit to accelerate its growth and for that reason, the share price is also increasing rapidly.
Step 3: Margin of Safety, calculate Intrinsic Value of Stocks
A great business can be a bad investment if you overpay for that. At the same time, even distressed debt (debt of an already declared bankrupt company) can be a good investment depending on how much you pay for it.
You must calculate the intrinsic value of the business you are buying. In simple terms, the intrinsic value of a business is the sum of all future Free Cash Flow discounted at a risk-free rate.
How to calculate Fair or Intrinsic Value of Stocks?
There are multiple methods and formulas available that you can use to calculate the intrinsic value of a business or stock. Intrinsic value calculation needs future projection. It is impossible to be accurate with estimation all the time. You should always use multiple methods to determine the intrinsic value.
We have implemented 5 stock’s intrinsic value calculators. We use all of the models whenever applicable. The resulting intrinsic value could differ a great deal depending on the model you use. We use the following methods to calculate intrinsic value.
- Valuation Matrix
- Benjamin Graham’s Number
- Peter Lynch Model
- Benjamin Grahams’s Intrinsic Value
- Multistage Dividend Discount Model
- Discounted Cash-flow model
Valuation Matrix Method
The use of valuation ratios is a very simple yet effective way to calculate the fair value of stocks. Everything has a tendency to revert to the mean value.
So, you can take 5-10 years mean value of the most used valuation matrix, buy a stock when it is undervalued and wait till the market returns to the usual mean value. Some most widely used valuation ratios are as follows:
- P/E – Price to Earning
- P/FCF – Price to Free Cash-flow
- EV/EBITDA – Enterprise Value / Earnings before Interest Tax Depreciation and Amortization.
- EV/EBIT – Enterprise Value / Earnings before Interest Tax
How Market has been Pricing AT&T since last 5 years?
| Year | P/FCCF | P/FCCE | P/FCF | P/CFO | P/E | P/BV | EV/EBITDA | EV/EBIT |
| 2020 | 5.89 | 5.58 | 8.16 | 5.19 | -39.19 | 1.17 | 11.17 | 60.90 |
| 2019 | 8.32 | 19.00 | 10.28 | 6.13 | 20.72 | 1.41 | 8.00 | 16.08 |
| 2018 | 7.56 | 6.30 | 9.72 | 4.98 | 10.00 | 1.07 | 7.12 | 14.89 |
| 2017 | 8.45 | 4.34 | 14.41 | 6.48 | 8.19 | 1.69 | 8.11 | 18.40 |
| 2016 | 13.70 | 19.39 | 16.37 | 7.05 | 20.33 | 2.11 | 8.44 | 16.22 |
| 5Y Average | 8.78 | 10.92 | 11.79 | 5.97 | 4.01 | 1.49 | 8.57 | 25.30 |
| 5Y Median | 8.32 | 6.30 | 10.28 | 6.13 | 10.00 | 1.41 | 8.11 | 16.22 |
Step 4: Paint the big picture
Most of the businesses are already expected to be filtered out by the end of Step 3. If a business passes step 3, then you must look into the qualitative measures.
Step 4 is about painting the big picture and seeing how this business fits into that picture. When you are painting the big picture, you must always investigate the following major aspects:
- Who are the major competitors
- What are the industry benchmarks
- How has the business been adopting its models with changing market condition
- Do they have purchasing power / good economic moat
Make a list of 3-4 main competitors and analyze their financials. Make them go through our model and see how they perform. If the business you want to buy does badly against their competitors eliminate it. Chose the competitor as your investment instead.
Different type of business has different type of numbers. For example, a utility business is very capital intensive thus their net margin and returns on capital will be much lower than an IT service business. The main reason is that IT services are contract-based and require less capital to get a contact. This does not mean that the utility business is a bad business and the IT service business is amazing. Just that their structures are different. So, always find the industry mean and use that data as the benchmark for your business.
Lack of adaptation according to industry and consumer behavior change is one of the main reasons for a business to become bankrupt. Remember Nokia, Blackberry, Polaroid! all great businesses yet went out of business. Look back into the history and see how this company adapted to the market changes over time. If you are confident that the management responds fast and correctly then go forward or leave it.
Step 5: Make a Bull and a Bear Case for each Investments
In the final step, you need to go into the incognito mood and investigate as much as you can. The two most important parts of step 5 are as follow
- Do a SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for Strength, Weakness, Opportunities and Threats.
- Accounting smell check. Try to find inconsistency or fabrication in the reported numbers.
When you are doing an accounting smell check look at the balance sheet and cash flow statement very carefully. Check for sudden big expense/income in the income statement. Find out what is the reason? Look for goodwill and any impairment charges. Try to justify the reasons. Look into the revenue diversification and the quality of the revenue of the business. Check for the debt maturity and possibly do a stress test. These checks above are only a few starting points for you to deep dive into.
You should also look at the current macro environment. There could be some short-term hick-ups and you may want to weather that before making an investment.
Finally, Always make a bear case (bad scenario) and a Bull Case (good scenario) for your investment thesis done above. Investment is a probabilistic game of risk versus reward. So, have a clear understanding of what could you lose if the base case happens and what could you gain if the bull case happens.
“Investing is not about being right or wrong, it is about possibilities”
Zakaria Khan
Concluding words
Investing is not easy and it is a case-by-case errand. It is very hard to generalize and make one single case that fits all. Our framework above merely provides a guideline.
Finding good investment is often a process of elimination and requires a lot of patience. Regardless of what type of investment you are making, make sure you understand that well enough. Your hard-earned money deserves only the best. Educate yourself, do your own due diligence and invest wisely. Make your money work for you.
Disclaimer: Investment is inherently risky. One may lose all his capital. I or KhanZ Invest AB does not provide financial advice. I wrote this article for your education and entertainment purposes. This is my point of view only. Stocks mentioned in this article are not recommendations they are just examples. Before investing, you must do your own research and understand the business you are investing in. For financial advice consult your certified financial advisor.

Pingback: mostbet mexico